2025-09-22
Whenever solar panels, batteries, or wind turbines are mentioned, one crucial element is often forgotten—the energy storage converter. Yet without it, the entire process of storing and discharging electricity in a cost-effective way would be impossible. So what is an energy storage converter, and why is it among the most talked-about terms in today's new generation renewable energy sector?
An energy storage converter is a type of power electronic device that regulates the two-way flow of electricity from an energy storage system (like lithium-ion batteries) to the power grid or proximate loads. It can be envisioned as the "translator" that enables stored DC electricity to be properly delivered as AC power—or the reverse when recharging.
To off-grid or hybrid systems, the converter is the connection that makes flexibility, safety, and efficiency possible. Converters are "critical enablers" of grid flexibility and renewable integration, the International Energy Agency (IEA) states (IEA, 2023).
Imagine a massive outdoor battery pack without a converter. The battery is able to store energy, but you would be unable to supply your devices easily, illuminate a village, or stabilize the grid. The converter does this by:
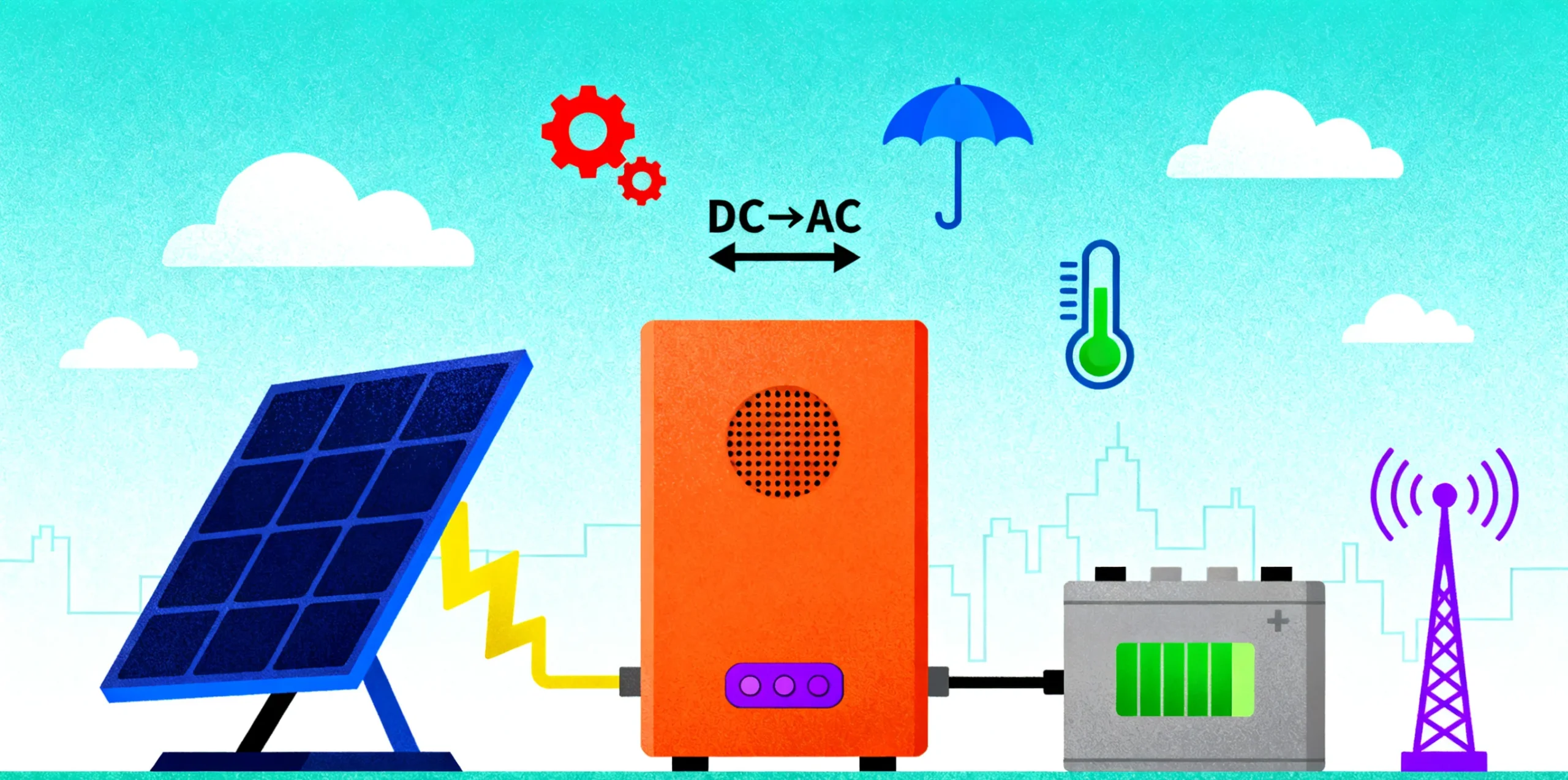
One of the trends that must be highlighted is the rising use of the outdoor energy storage converter. The products are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions while in use in isolated or industrial environments. For example:
So, when the question is: Do I need an outdoor energy storage converter?, the answer depends on whether the system is going to be exposed to environmental stress and must be free to work without maintenance.
To have a clearer picture of the operation of such devices, here's a simplified overview:
1.DC/DC Conversion – Regulates charging of batteries with adjusting input voltage and current.
2.DC/AC Inversion – Inverts stored DC electricity to useful AC power for household consumption or the power grid.
3.Bidirectional Power Flow – Enables charging and discharging through one device.
4.Energy Management Integration – Regulates an EMS (Energy Management System) to realize its optimal performance.
Think of it this way: the converter is the brain and heart of a storage system—driving electricity to where it's required, while making smart decisions in real-time.
The future of energy storage converters is moving toward:
Next-generation converters will reduce system costs by up to 15% over the next five years, reducing the cost of storage across the world, BloombergNEF's 2024 energy storage forecast (BloombergNEF, 2024) estimates.
At Shenzhen, China, a home microgrid employed an outdoor energy storage converter system having a 1MW lithium-ion battery pack. The converter supported solar charging during the day and night power together with smoothing the grid during peak load. This system reduced the occurrence of blackouts by 30% in the area, reflecting the significance of converters in real performance.
| Feature | Energy Storage Converter | Standard Inverter |
| Bidirectional Power Flow | Yes | Mostly No |
| Integration with EMS | Yes | Limited |
| Supports Grid Services | Yes (frequency/voltage) | Rare |
| Outdoor Versions Available | Yes | Less common |
One of the readers might query: isn't an energy storage converter just another inverter? Not exactly, in fact. While both do DC to AC conversion, the converter is bi-directional and far more specialized, i.e., it also controls charging batteries.
Another general assumption is: do I need one for my home solar installation? If your system has batteries and you desire optimal efficiency, then yes—you'll see the advantage of a converter. However, if you're grid-connected with no storage, a basic inverter may suffice.
And are they really needed, finally? If your electronics and batteries are going to be exposed to the weather—ie, rural, industrial, or off-grid projects—then yes, they can save you from expensive failures.